
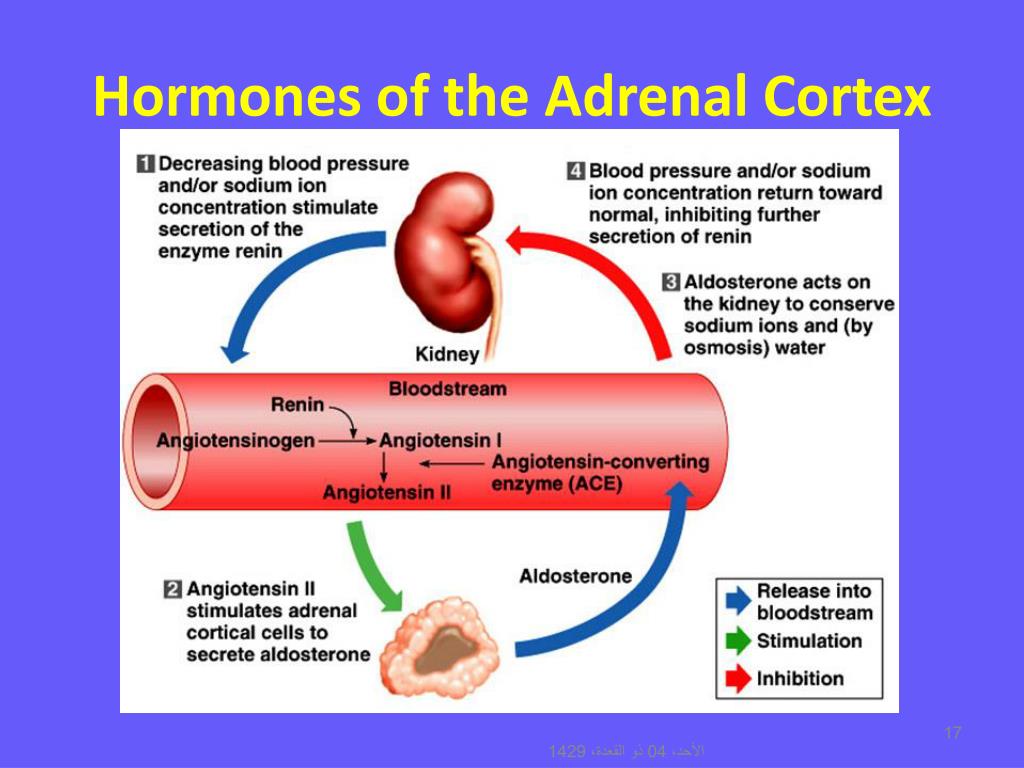
Secondly, ACTH and its precursors contain melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH)-like peptide sequences, which can mimic MSH and cause hyperpigmentation. Firstly, low cortisol stimulates increased ACTH production. The reason for this is to do with the lack of negative feedback from cortisol to the hypothalamus and pituitary, and the structure of ACTH and its precursors. Patients also show postural hypotension, which is caused by mineralocorticoid deficiency.Ĭlassically, they demonstrate hyperpigmentation, or ‘ bronzing’ in the palmar creases of the hands and flexor surfaces of joints and on the face. Patients present with various symptoms, including tiredness, weakness, nausea and vomiting. It accounts for 80% of cases of hypoadrenalism in the UK. Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid which regulates sodium and potassium levels in the blood, thereby regulating intravascular volume. This is an autoimmune disease whereby the immune system targets the adrenal glands, resulting in reduced cortisol and aldosterone production.

Regulate behaviour, mood and cognition through activity on the CNS.Regulate calcium absorption from the gastrointestinal tract.Bone metabolism – acts on trabecular bone to limit osteoblast activity to make new bone.Cortisol increases plasma glucose levels by breaking down proteins to amino acids to be taken to the liver, as well as by stimulating gluconeogenesis in the liver.A summary of the effects of cortisol is listed below: Cortisol exerts its effect on many tissues including the liver, fat, muscle, bone, skin and others.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
